When aspiring analyst starts to learn about documenting the project’s requirements, they are bound to come across terms like Business Requirements Document (BRD), Software Requirement Specifications (SRS) document, and Functional Requirement Specifications (FRS) document.
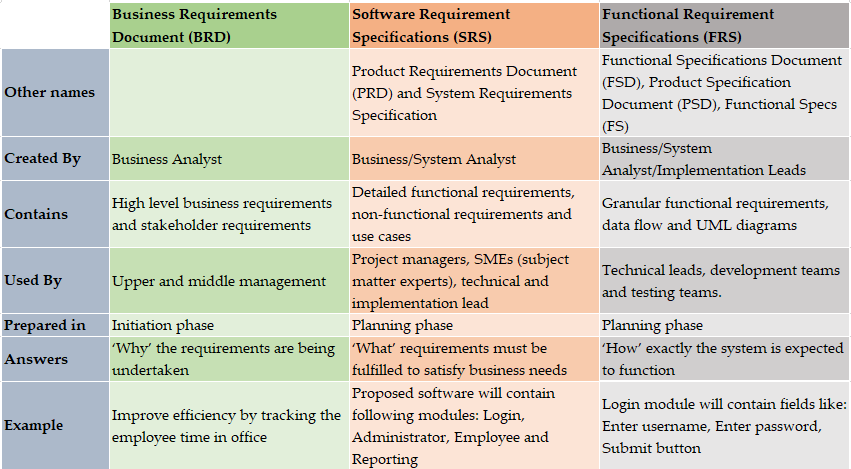
If you are looking for a quick comparison between the three, then here you go:
- BRD contains ‘high-level’ business requirements,
- SRS contains ‘detailed’ functional and non-requirements
- FRD/FRS contains ‘granular’ functional requirements along with data flow and UML diagrams.
However, if you would like to understand the subtle differences and uses of all three documents, please read on…..
Business Analysis is governed by specific defined standards and frameworks that should be followed to conduct practical analysis of requirements in any project. However, there are no universally accepted guidelines for BRD, SRS, and FRS in any body of knowledge (BABOK, CMMI) regarding their overall structure (format), contents, and level of detail. Thus, this results in organizations modifying these requirement documents based on their processes & standards, the resource available to them, and the type of project.
The side-by-side comparison below aligns with the most widely accepted business analysis and project documentation practices:
[Please click the image to expand]
Business Requirements Document (BRD)
A BRD is one of the most widely accepted requirements documents, and BABOK, the globally recognized standard for the practice of business analysis, defines it as:
A Business Requirements Document (BRD) is a requirements package that describes business requirements and stakeholder requirements (it documents requirements of interest to the business, rather than documenting business requirements).
Example: One of the statements in the BRD could look like – The Company would like to improve its efficiency by tracking the time spent by the employees on different activities.
BRD is usually one of the first few documents created in the project
Additionally, the BRD also contains the needs of a specific/group of stakeholders that will interact with the final service or product. Thus, it answers the ‘Why’ part of the requirements (and not ‘What’ or ‘How’), i.e., why the requirements are being undertaken and what results are expected from the system? It should be noted that all future requirements, enhancements, and change requests against the project should be justified by the company’s (or business’s) goals and needs listed in the BRD.
A BRD is always prepared by the business analyst on the project and is created after performing an analysis of the client company and talking to the stakeholders. Once a BRD is prepared, it’s often reviewed and signed off by the client to ensure it correctly captures the business’s expectations and the key stakeholders.
The primary audience of the BRD
Software Requirement Specifications (SRS) Document
Once it has been identified ‘why’ the project is being undertaken (by creating the BRD), it’s now time to document ‘What’ requirements must be fulfilled to satisfy the business’s needs.
A Software Requirement Specifications (SRS) document is a detailed and structured requirements document that contains the functional requirements (illustrates behavior), non-functional requirements (depicts characteristics) along with any use cases that the software must fulfill.
Example: The proposed software to track the employee’s office time will contain the following modules:
- Login Module: Will authenticate the user based on the login credentials entered and allow only the registered users to login.
- Administrator Module: Will contain the features that will allow an admin to manage the users – Add user, edit users, delete/inactivate user, add/edit user permissions, group users, add projects, etc.
- Employee Module: Will include the features that will help the employee enter his effort details – Enter/edit effort spent, enter/edit task details, choose the project, edit basic details, reset the password, view previous effort details, etc..
- Reporting Module: Module exclusive to the administrator and will allow them to extract aggregated time and effort reports against users, projects, and tasks. Furthermore, the admin should be able to export these reports in .xlsx and PDF formats.
SRS is one of the vital documents in any project as it bridges the gap between what business wants and what they will get by documenting the broad layout, characteristics, and workflows of the software being developed. Since a software’s major requirements are clearly organized and elaborated in an SRS, it’s commonly used for estimating the cost and effort required for developing that software. At times, it’s even used as a contractually binding document between two parties since it contains enough details to reach an agreement.
You can view an SRS as a document that ‘elaborates’ the BRD’s high-level statements into a module, sub-module, and features without going in-depth on each page.
The systems analyst of the project prepares the SRS; however, if a systems analyst is not available, it may even be prepared by the business analyst. To prepare an SRS, the analyst has to conduct requirement elaboration sessions with the relevant stakeholders, meticulously analyze all the aspects of the software being developed and then list down the requirements against each one of them. It’s ensured that every listed requirement in an SRS should fulfill the business objectives listed in the BRD.
The primary audience of the SRS is the project managers, SMEs (subject matter experts), technical and implementation lead responsible for overseeing the development of the listed functionalities.
Other names – Product Requirements Document (PRD) and System Requirements Specification
Note – Some organizations or small projects do not create an SRS and just elaborate their BRD to accommodate the functional, non-functional requirements and use case details.
Functional Requirement Specifications (FRS) Document
The FRS document is the most detailed and granular document of the three. It finally describes ‘How’ exactly the system is expected to function to satisfy all the requirements listed in the BRD and SRS.
A Functional Requirement Specifications (FRS) document is a granular and low-level document that elaborates all the details around the functional requirements on a project.
Example: The Login module will contain the following fields
- Enter Username: This field is a textbox that will allow the user to enter the username, which is their registered company’s email ID.
- Enter Password: This field is a textbox that will allow the user to enter the password. The entered password should not be shown to the user and should be encrypted as a ‘*’.
- Submit button: This button, when clicked, will validate whether the entered credentials are valid. In case either the username or the password is incorrect, the system should display an alert message ‘Incorrect Username or Password’……
The FRS document is very descriptive and elaborates on all the functional requirements (including business, compliance, security requirements, etc..) unambiguously by specifying all the fields and user interactions on every page of the software being built. Also, to aid better comprehension, process flow diagrams, UML diagrams, and wireframes are added to the FRS.
It should be noted that the FRS document is created from the perspective of a user and describes how the software will behave when an external user interacts with it. The development team refers to this project artifact to understand what exactly they have to build and the testing/QA team to know what are the different scenarios & test cases on which the software should be tested.
The FRS is prepared by the business/systems analyst on the project, and post-completion, it’s reviewed by the project manager. After that, the FRS is shared with the clients for a final review, and once approved, this document becomes a standard document (aka baseline) that defines the way the software is to function.
The primary audience of the SRS is the technical leads, development teams, and testing teams.
Other names – Functional Specifications Document (FSD), Functional Specification (FS), Product Specification, and Functional Specs.
FREE KIT DOWNLOAD: Get BA Documents Template Toolkit!!
Our free Template Toolkit contains the following professional, pre-formatted, and ready-to-use Business Analyst Document templates:
- Use Case Document Template
- Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) Template
- Requirement Management Plan Template
- Project Vision Document Template
- Test Case Template
